Integration types
When integrating with Salto KS, every client application needs to go through an authentication process before making a call to the APIs. This is done so that the KS Identity Provider, which works as a security gateway, is able to verify the identity of the application that is trying to connect.
Every client will receive a client ID and, depending on the application type they are building, a client secret, which is configured for the specific OpenID Connect flow they will use. These flows are sometimes referred to as grant types. They are not specific to the Salto KS platform, but rather an implementation of the public OpenID Connect protocol, which is also used by other systems on the internet. Libraries and frameworks that implement OpenID Connect protocol can also be used by partners integrating with the Salto KS platform.
The OpenID Foundation website has a list of different OpenID Connect implementations.
Using a client library is recommended as it handles different flows automatically and it will be updated when the OpenID Connect protocol changes for any flow. This can happen if a security vulnerability is discovered, and the protocol standards need to be modified.
There are five (5) possible client integrations with the Salto KS Connect API: web client, mobile iOS client, mobile Android client, mobile cross-platform client, and backend server. These integration types can be grouped into two categories: interactive and non-interactive.
Interactive integrations: web clients and mobile clients
Interactive integrations correspond to clients that are building:
Web-based applications, such as Single Page Applications (SPAs).
Mobile-based applications, which can be native integrations such as for iOS and Android, or cross-platform integrations for frameworks like Flutter or React Native.
These applications have a user interface (UI) component, through which clients interact by making use of an authorization_code flow.
The authenticity of the client making the request is ensured with the client ID and the predetermined URLs that are registered in the system.
The return URLs are attached to the specific client ID, and this is where the results of the requests are delivered.
The authorization_code flow consists of two components:
a front-channel step (for example, a login page) and a back-channel step.
The operation performed in the front-channel generates an authorization code, which is then exchanged in the back channel with the requested token.
Interactive clients can be either public or confidential.
For both cases, the authorization_code flow is used together with a Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE), which is a security requirement to keep the flow secure.
The difference is that for confidential clients, a client secret is also required when providing the credentials.
The client secret must be known for the authorization code to be turned into an access token.
The authorization_code flow happens between the client application and the Salto KS Identity Provider, and it can be broken down into the following steps:
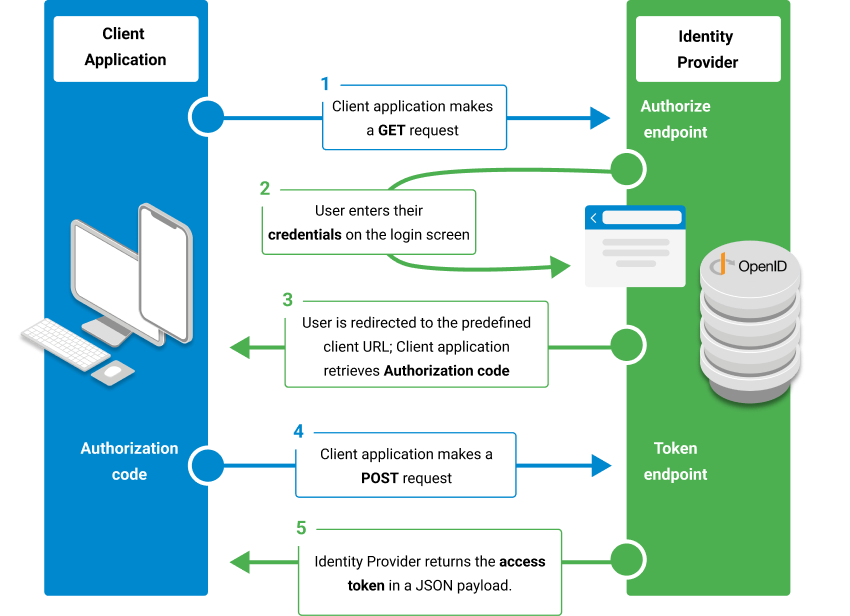 Authorization code flow
Authorization code flow
With the access token, the client application can make a call to the KS Connect API.
Furthermore, if the GET request in step 1 contains the scope offline_access, then the Identity Provider will return not only an access token, but also a refresh token in step 5.
curl --location \
--request \
GET "https://{{identity-server-url}}/connect/authorize?response_type=code&scope=user_api.full_access+offline_access&client_id={{client_id}}&redirect_uri={{redirect_uri}}"Clients building interactive integrations that implement the Salto KS Digital Key functionality can also choose to extend that to users without a profile in the KS platform, a feature known as Digital Key for Guests.
This can be applicable to different use cases, for instance in Hospitality or Co-living businesses, in which a user who has a Salto KS profile wants to invite someone over for the day.
They can send an invitation to that person so they can generate their own anonymized Digital Key that does not require a KS profile to be created.
In this scenario, the integration will make use of the access_code flow.
It is important to first mention that, for the access_code flow to be possible, the user that is registered in the KS platform must be part of a Pod and have a pod_member role.
When setting up the integration, clients must create a POST request to the Salto KS Identity Provider to ask for an access token, which will be returned to the client application (that is, the user with a KS profile).
With that, the client application can request an access code from the Connect API.
The returned access code is what will be shared with the person who is being invited to download a Digital Key for Guests, without a KS profile.
On the front channel, this access code can be implemented to be returned in the format of a URL link, so it is easier to be shared.
With the access code at hand, the application of the person without a KS profile will be able to call the Identity Provider to get an authentication token and then, be able to call the specific endpoints to generate their Digital Key for Guests.
Note that authentication tokens generated from an access code can only be used to generate a Digital Key, nothing else.
The access_code flow is meant to be implemented in mobile applications, since the KS Digital Key can only open Salto locks via Bluetooth connection.
The only scenario in which we recommend the implementation of Digital Keys in browser applications is if they can open a Bluetooth channel to establish communication with Bluetooth Low Energy devices.
Non-interactive: backend server
Non-interactive integrations correspond to clients building a backend server integration, which does not have a UI component. In other words, it works as a server-to-server interaction.
The KS Connect API always works with the concept of a user, which also applies for backend integrations.
For this reason, server-to-server interactions need a predefined user.
For instance, this can be a system user that needs to be previously added to all the sites the client wants to manage.
In this case, the system user needs to be added under a site_admin role.
Non-interactive clients make use of a password flow.
Once the environment is set up, clients must create a POST request to the Salto KS Identity Provider to request the token, as well as provide a client ID and a client secret.
Then, in the body of the request, the client must fill in the following values:
curl --location --request POST "{{identity_server_url}}/connect/token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
--header "Authorization: Basic Y2xpZW50X2lkOmNsaWVudF9pZF9zZWNydGV0" \
--data-urlencode "grant_type=password" \
--data-urlencode "username=(insert KS email here)" \
--data-urlencode "password=(insert KS password here)" \
--data-urlencode "scope=user_api.full_access"The response body will contain the access token with which clients can make API requests.
Refresh tokens
Refresh tokens have a much longer lifetime, so they can be used to obtain another access token with a POST call to the token endpoint.
This flow works for both interactive and non-interactive clients.
curl --location --request POST "{{identity_server_url}}/connect/token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer {{access_token}}" \
--data-urlencode "client_id=client" \
--data-urlencode "client_secret=secret" \
--data-urlencode "grant_type=refresh_token" \
--data-urlencode "refresh_token=hdh922" Back
Back
